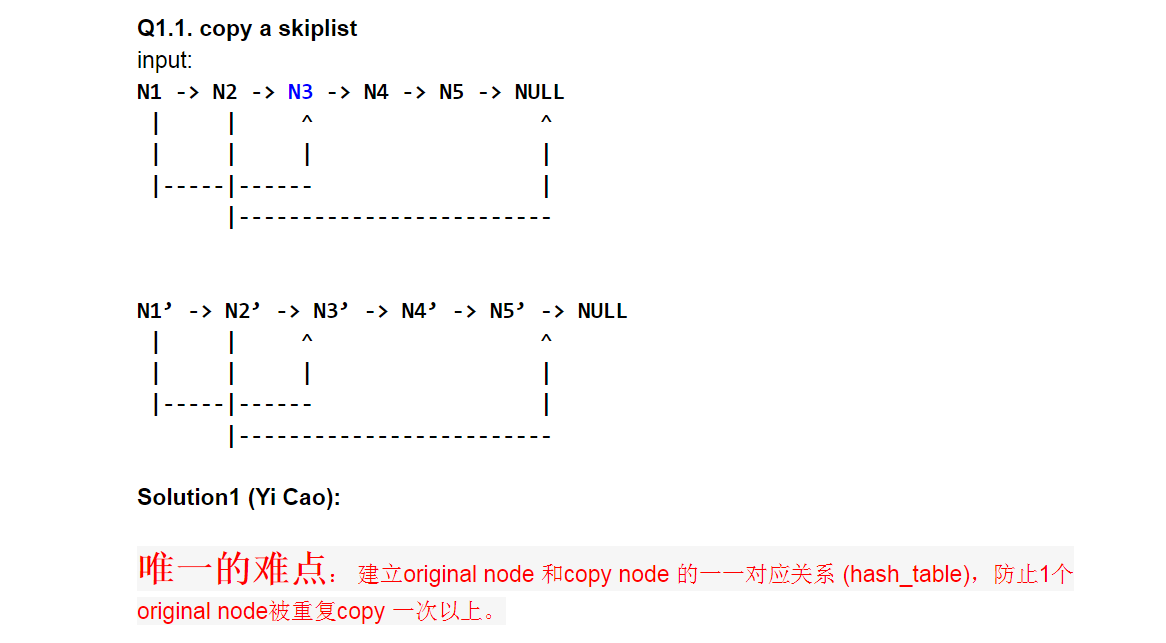
hashmap 记录original node and copy node 的对用关系,在copy 每个node前检查是不是已经在hash table
思路:
seperate into 2 steps, copy linked code, and then copy the random pointer node if capable. Each time to copy the node, check whether already in the hashmap<OriginalNode, CopyNode>, if exist, just get it from hash table, otherwise generate new one and put the new set into the hash table.
Another trick to simplify coding is the dummy node.
/**
* class RandomListNode {
* public int value;
* public RandomListNode next;
* public RandomListNode random;
* public RandomListNode(int value) {
* this.value = value;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public RandomListNode copy(RandomListNode head) {
/**
* class RandomListNode {
* public int value;
* public RandomListNode next;
* public RandomListNode random;
* public RandomListNode(int value) {
* this.value = value;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public RandomListNode copy(RandomListNode head) {
// Write your solution here.
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
// use map to store orignal and new node mapping
Map<RandomListNode, RandomListNode> lookup = new HashMap<RandomListNode, RandomListNode>();
RandomListNode dummy = new RandomListNode(0);
RandomListNode cur = dummy;
while (head != null) {
if (!lookup.containsKey(head)) {
lookup.put(head,new RandomListNode(head.value) );
}
cur.next = lookup.get(head);
if (head.random != null) {
//copy the random node
if (!lookup.containsKey(head.random)) {
lookup.put(head.random,new RandomListNode(head.random.value));
}
cur.next.random = lookup.get(head.random);
}
head = head.next;
cur = cur.next;
}
return dummy.next;
}
}